We can outline motivational thoughts because of the wishes, needs, associated interests that arouse or activate an organism and direct it toward a selected goal. It will either steam from internal or external sources or from the interaction of each. For instance, the need for food or sex stems from individual biological desires. On the opposite hand, the will for social recognition or honor stems from external sources. However, generally, it will be streamed from the interaction of each external and internal source.
For instance, if somebody feels like food, this comes from his internal drives. However by what style of food he desires to satisfy the hunger altogether depends on his alternative meaning it came from an external supply. You have got to prime the pump and find the juice flowing, which motivates you to figure on your goals.
Human beings have interaction in numerous varieties of activities and there are motivational thoughts behind these actions. For example, a person is endeavoring for obtaining employment, a student is finding out his books for obtaining an honest result, an individual is feeding a meal then on. Behind these actions, there’s a reaction that compels that person to try to do action-that is termed motivational thoughts.
The aim of obtaining high marks may be motivational thoughts for the coder. Similarly, the aim of earning cash may be motivational thoughts for the person and that’s why the person is endeavoring to obtain employment.
Motivational Thoughts and Motives
Though we predict that motivational thoughts and motives are a similar term and use them interchangeably, that’s not right. They’re connected however they don’t have a similar meaning. Motivational thoughts that the psychological development that’s any reasonably general behavior and the motive is that the concrete reason for taking any action. There are three varieties of motives. They are biological motives, social motives, and private motives.
Motivational Thoughts Cycle
Motivation thoughts cycle may be a transition of states among associate organisms that energizes the organism toward the satisfaction of a selected wish. Motivational thoughts themselves are taken into account in a hypothesized state. Psychologists use the thought of got to describe the psychological feature properties of behavior.

Four completely different states comprise motivational thoughts that take place in the associate organism to drive him towards every action. Owing to a selected wish, every action is initially initiated. The necessity drives the person into taking action.
Because of the action, positive results cause later action acts as associate incentive motivating an individual towards the goal. However, no one stops when achieving sure goals, another goal is targeted then and this development continues on and on. This development has been termed the psychological feature Cycle.
Need
Need is termed a scarcity or deficit of some necessity that ought to be consummated by doing target tasks. It’s a state of physical deprivation that causes tension among associate organisms. The strain caused once the organism is bereft of basic wants of life as food, water, and sleep, causes the interior atmosphere of the associate organism to be unbalanced. The imbalance caused by the necessity arouses the organism to take care of its balance. Would like the initial condition or stimulating issue for any goal-directed behavior.
Drive
Need ends up in the drive, that is the second step towards achieving a goal. Drive will be outlined because of the state of tension or arousal created by would like. The drive may also be thought-about because of the original supply of energy that activates associate organisms. As an example, once an associated organism is hungry and/or thirsty, the organism seeks to scale back this drive-by feeding and/or drinking.
The drive acts as robust persistent information to push associate organisms towards their goal. It’s the state of heightened tension resulting in restless activity and preparative behavior.
Incentive
The incentive theory rests on the belief that individuals are actuated by a drive for incentives and reinforcement. The behaving organism is aware of well concerning his actions and therefore the consequences that may be received from that action.
The idea additionally understands incentives because the motivation inspires an individual to realize any explicit goal object. For example behavior like a drink is an associated incentive that reduces the thirst of the person caused by the necessity to satisfy his drive. The reduction of behavior then causes the balance in the associated organism.
According to Hilgard, motivation is some things within the external atmosphere that satisfies the necessity and therefore reduces the drive through consummative activity.
Goal
The goal of any actuated behavior is that the reduction of tension within the body will be thought-about as a goal. For example: once a person becomes hungry, that man chuck food, and his body restores to a balanced condition and therefore reduces the strain. This reduction of tension causes associate energized activity that’s referred to as a goal. Once the goal has been completed, the organism is once more prepared for one more goal-motivated behavior.
Goals will be positive or negative. Positive goals are that varieties of goals wherever an associated organism tries to achieve, like sexual fellowship, food, ending, etc. Negative goals at the other of positive goals that may be understood by associate organisms attempting to flee from or avoid, like embarrassing things, punishments.
Two Varieties of Motivational Thoughts in Life
There are Two varieties of motivational thoughts. They’re intrinsic motivational thoughts and extrinsic motivational thoughts.
1. Intrinsic Motivation
During this style of motivational thoughts, motives originate from within the body of organisms. Internal driving state stimulates a person to behave during an explicit method. Every kind of biological drive like hunger, thirst, sleep, relief from pain, temperature regulation includes in it.
2. Extrinsic Motivation
During this style of motivational thoughts, motives originate from within the body of organisms. The drive outside the body stimulates the organism to behave or to try to do the action. It includes incentives, bonuses, allowances, promotion and change, rewards, and punishments.
Other varieties of motivational thoughts- Positive and negative incentives.
Theories of Motivational Thoughts
No single motivational thoughts theory will justify all aspects of people’s motives and there also are several theorizers who explained their theory otherwise. Every theoretical rationalization will function the idea for the event of techniques for motivating an individual. There are several theories of motivational thoughts. They are-

Hierarchy of Desires Theory
Abraham Maslow’s hierarchy of desires is the known theory of motivational thoughts. He knows 5 desires in human-being. the first 5 desires in human-beings are:
1. Physiological Needs
Physiological desires includes hunger, thirst, shelter, sex, and alternative bodily desires.
2. Safety-Security Needs
Security and protection from physical and emotional damage and guaranteeing safety from any forms of threats.
3. Social-Belonging Needs
This includes tenderness, belonging, acceptance, and friendly relationship.
4. Esteem Needs
There are 2 factors of shallowness. They’re internal factors and external factors. Internal factors like pride, action, and external factors like standing, recognition.
5. Self-Actualization Needs
Drive to become what we have a tendency to be capable of becoming; includes growth, achieving our potential, and self-realization, the best level of the hierarchy pyramid.
According to Maslow, when satisfying one would like, consequently become dominant. after you need to inspire somebody, you would like to grasp what level of the hierarchy that person is presently on and specialize in satisfying desires at or higher than that level. Maslow’s theory received long-standing wide recognition. It’s intuitively logical and simple to grasp and there are several analyses that have valid points.
McClellan’s Theory of Needs
David McClelland gave a theory of motivational thoughts engineered on this and his 1961 book, “The Achieving Society. There are three desires all told to people. They are a desire for accomplishment, a desire for affiliation, and a desire for power. Totally different individuals have different characteristics looking at their dominant incentive.
According to McClellan, these motivational thoughts are learned which is why it’s known as the Learned desired Theory.
Achievement
All individuals have a desire for accomplishment. Individuals who are driven by accomplishment work terribly effectively either alone or with alternative high achievers to realize their goal.

When providing feedback, they offer achievers a good appraisal. They require to understand whether or not they are doing right and wrong – so they’ll improve.
Affiliation
People are driven by affiliation work best in very cluster surroundings, so they’ll attempt to integrate them with a team (versus operating alone). Once providing feedback, they offer feedback in person.
Power
Those with a high want for power work best once they are guilty and take a look at to realize their goal by hook or by crook.
Goal-Setting Theory
The goal-setting theory explains that specific and tough goals, with feedback, facilitate the United States of America to do our greatest performance. Goal setting helps the United States of America to develop AN action set up that inspires and guides an individual or group toward achieving a definite goal. Edwin A. Locke and his colleagues have shown that a lot of specific and bold goals lead the United States of America to a lot of performance improvement than simple or general goals.

Goal setting is the set of activities that are followed to realize one thing. In goal-setting theory, projected by Edwin Locke, he reveals the spectacular effects of goal specificity, challenge, and feedback on performance. Once goals square measure tough, the person tries to perform their best to realize his goals. Tiny and straightforward goals slim one’s performance.
Goal settings are often full of outcomes in four major ways that. They are:
Choice
When making various, goals can slim someone’s attention and direct them toward goal-relevant activities and fromward them goal-irrelevant actions.
Effort
To achieve a goal somebody becomes a lot toilsome. As an example, if somebody sometimes will do ten maths per hour however desires to try and do fifteen maths per hour, then they’ll work tougher to provide a lot of widgets than while not that goal.
Persistence
Because of this goal somebody has become a lot more willing to figure through setbacks.
Cognition
Goals help somebody to develop and alter their behavior in keeping with their goal.
Equity Theory

A theory that claims that people are driven by fairness. In keeping with this theory, one compares one’s job inputs and outcomes with those of others so answers eliminate any inequities as a result of they require equality in all told aspects. In keeping with this equity theory, staff who understand inequity can create one amongst five choices:
- Change Inputs: If one underpaid, he can provide less effort or if overpaid, can provide a lot of effort.
- Change Outcomes: One who gets rewarded on doing a science, he can do a lot of math then.
- Distort Perceptions About One’s Ownself: “I want to assume that I’m not that abundant smart in psychological science, however currently I notice I work heaps tougher than everybody else does”.
- Choose a Different Referent: “I am not pretty much as good as my brother in doing art, however, I’m doing heaps higher than Salim”.
- Leave the Field: Quit the work by leaving the workplace.
Organizational Justice
Organizational justice composed of distributive, procedural, informational, and social justice within the geographic point.
Distributive Justice
Distribution ought to be equal within the geographic point so no one will question fairness. So, during this approach perceived fairness of the quantity and allocation of rewards among people ought to be ensured. Example: I got the promotion that I merited.
Procedural Justice
The perceived fairness of the method ought to be maintained by distributing the rewards equally within the organization. Example: Eid Bonuses are given equally among the workers.
International Justice
The perceived degree to that one is treated with dignity and respect and this could be ensured for everybody within the organization. Example: At the time of talking with my boss, once telling him regarding my raise, he was terribly nice and complimentary.
Model of Structure Justice
Organizational Justice Definition: overall perception of what’s truthful within the geographic point Example: I believe this can be a good place to figure.
Expectancy Theory
This theory explains that the strength of a bent to act in a very bound approach depends on the strength of an expectation that the acts are going to be followed by a given outcome.
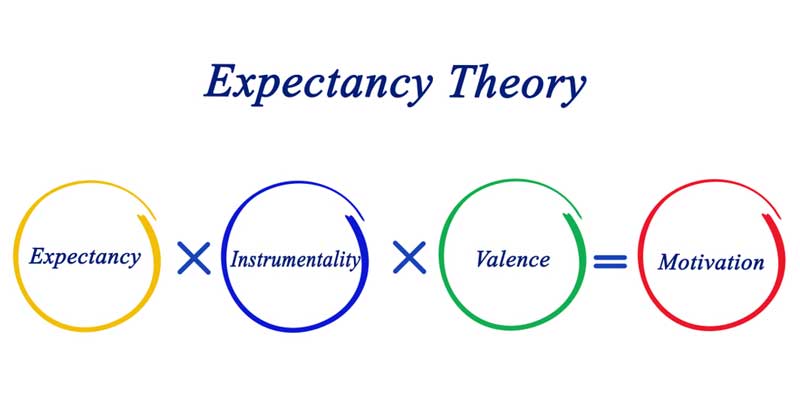
Victor Vroom’s expectancy theory of motivational thoughts is the most generally used theory of motivational thoughts. Although their square measure several criticisms of this theory have been created, most of the idea proof supports the idea. Expectancy theory suggests that the approach of acting in a very bound approach depends on the strength of our expectation of a given outcome and its attractiveness.
In sensible terms, the staff is going to be driven to figure and exert a high level of effort once they believe that it can result in an honest performance appraisal which will result in structured rewards like earnings will increase and or intrinsic rewards, which the rewards can satisfy their personal goals. The theory focuses on three relationships:
1. Effort–Performance Relationship
The individual perceived that exerting a given quantity of effort can result in performance.
2. Performance–Reward Relationship
The degree to that the individual performs, can result in the attainment of a desired outcome.
3. Rewards–Personal Goals Relationship
The degree to which that structure rewards satisfy an individual’s personal goals or desires and therefore the attractiveness of that reward for the individual.
Motivational Thoughts vs. Feeling
Although motivational thoughts and feeling square measure in and of itself coupled, they’re two essentially various things. Motivational thoughts describe the wishes, desires, or desires that direct an individual to behave in a very explicit approach toward a goal; in distinction, a feeling could be a subjective state of being which will be delineated as a sense.
Feeling and motivational thoughts each influence behavior and that they conjointly lead the United States of America to require action. Feeling acts as an incentive. As an example, the feeling of concern will inspire an individual from the item that fears him. Whereas the feeling of happiness inspires an individual to be a lot productive on a project that reinforces that feeling and continues the act that produces his happiness.
Conclusion
Motivational thoughts are a vital issue for reaching a definite goal. Motivational thoughts play a vital role in all told spheres of life. Motivational thoughts energize organisms to act in a very bound approach and to become goal-minded. In an organization, it’s necessary to inspire staff to realize the goal. It’s conjointly necessary for instructional sectors too.
References:
https://www.goodmorningquote.com
https://www.goodmorningquote.com




