Motivation Psychology is that basic psychological method. None would deny that it’s the foremost vital method within the additional small approach to structure behavior. Many folks equate the causes of behavior with motivation. Causes of behavior square measure a lot of broader and additional advances than are often explained by motivation alone. Then motivation psychology ought to ne’er be under-rated.
On the side of Perception, temperament, and Learning, Motivation psychology could be a vital method in understanding behavior. It should be remembered that motivation shouldn’t be taken with a pinch of salt because of the sole rationalization of behavior. It acts and interacts in conjunction with alternative mediating methods and therefore the atmosphere.
It should even be remembered that like all alternative mediating processes or atmospheres, motivation can’t be seen. Motivation psychology is invisible. What all are often seen is that behavior. Motivation psychology is that theoretical construct that’s wont to facilitate making a case for behavior. Then it ought to ne’er be equated with the behavior.
What Is Motivation Psychology?
Motivation Psychology is an urge or impulse that influences a person to do something to achieve a certain goal, wish, desire.
It’s what causes you to act, whether or not it’s obtaining a glass of water to scale back thirst or reading a book to achieve data.
Motivation Psychology involves the biological, emotional, social, and psychological feature forces that activate behavior. In everyday usage, the term “motivation” is often used to describe why someone will one something. It’s the actuation behind human actions.
Motivation Psychology does not simply confer with the factors that activate behaviors; it conjointly involves the factors that direct and maintains these purposeful actions (though such motives square measure seldom directly observable). As a result, we regularly ought to infer the explanations why folks do the items that they are doing supporting evident behaviors.
What precisely lies behind the motivation psychology for why we tend to act? Psychologists have projected totally different theories of motivation psychology, as well as drive theory, instinct theory, and humanistic theory (such as Maslow’s hierarchy of needs). The fact is that this square measures many alternative forces that guide and direct our motivations.
The meaning of motivation psychology: these days just about, all as well as laymen and students have their own definition of motivation psychology, containing one or a lot of of the subsequent terms: needs, Wishes, Aims, Goals, Needs, Drives, Motives, and Incentives. Technically motivation is derived from the Latin word “Movere” meaning ‘to move’.
Definition: A motive is associated with Nursing’s inner state that energizes, activates, activates, or moves (Hence motivation), that directs or channels the behavior towards the goals. A motive is a restlessness, an absence of you, a force. Once in the grip of a motive, the organism will do one thing. It most typically will do one thing to scale back the restlessness, to remedy the shortage, to alleviate to mitigate the force. The key to understanding the motivation looks to exist which means and the relationship between wants, drives, and goals. The basic motivation method sets-up drives to accomplish goals.
Motivational Psychology Cycle
The Desire for the issue is followed by the action to urge the specified factor that eventually ends up in the attainment of the thing. If the necessity of occupation the cycle isn’t totally glad, it’ll move once more to search out its finish. And if it’s achieved its motives it then finds new motives to satisfy its new desires and follows a constant pattern and starts the cycle once more.
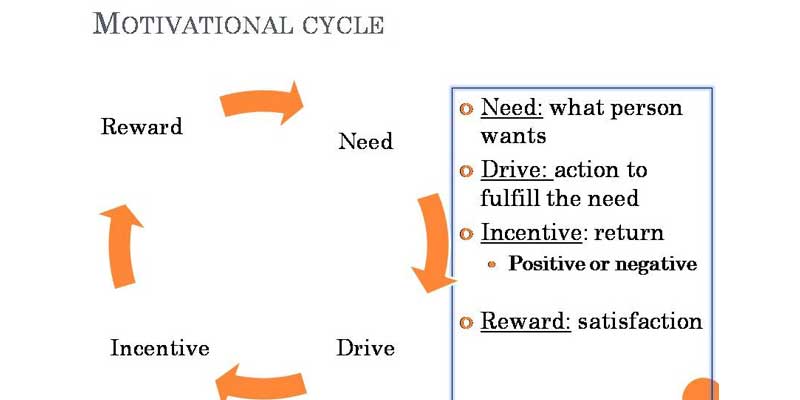
This circular motive renowned is understood as a thought because the “Motivation Psychology Cycle” this method is known once a private perpetually try to satisfy their needs or wishes following in an exceedingly cycle around would like, Drive, Incentive, and Reward.
1. Need
Need is that the physical or psychological deprivation of the body to form the requirements. It’s the dearth of what we wish or would like. Once the stimuli remain constant we have a tendency to don’t feel like it. The tendency to revive a balanced condition within the body is thought of as equilibrium. It’s characterized by physiological functioning.
The aroused condition motivates the organism to imitate behavior to remedy the necessity. For instance, the one that is hungry desires food. Similarly, an individual might need power.
This shows psychological features would have 2 categories: physiological (primary) or psychological (secondary). Physiological desires are basic wants while not that organism can’t live, for instance, would like for food, rest, oxygen, water, etc. Psychological would like is said to be the individual happiness and well-being. For instance, love, power, prestige, recognition, status, etc.
2. Drive
An indoor motivation psychology state that’s created by a desire maybe a drive. For instance, a hungry person seeks food to satisfy his or her desires. Drives are the action-oriented element or the motion to meet the will of the intended behavior. Hunting for food by a hungry person is translated into hunger drive. Drive will activate over one response. Drive is that the internal tension state that builds up till they’re glad.
3. Incentive
The third idea that moves around the motivation psychology cycle is an incentive. The incentive is that the acceptable object or scenario toward that intended behavior is directed. Incentive eases a desire and reduces a drive. It will give satisfaction to the aroused drive. For instance, food is the incentive for the hungry person.
It is something we’ve learned to value like cash, status, and therefore the approval of others. Incentives manage a lot of human behavior. Associate organisms can approach positive incentives, and avoid negative incentives. For instance, steamed food is a positive incentive for the hungry person and chocolate is a negative incentive because it won’t satisfy the hunger of the person.
4. Reward
Once the organism has obtained the inducement it drives pleasantness or satisfaction, that is that the reward. Reward restores the physiological condition. It brings readjustment. If the reward is achieved, the individual feels galvanized, and his or her performance can improve. For instance, food is a reward for a hungry one that feels alleviated and glad about it. Chocolates might not be his reward because they won’t satisfy his hunger. If an individual is totally glad the equilibrium take is achieved for that specific would like.
We know that a person has unlimited needs, desires, or needs. As before long collectively would like is glad another crop up. The person begins to figure (or get motivated) to meet that need and this ends up at the start of the latest motivation cycle. Therefore this cycle ne’er stops, it goes on and on. If the necessity occupation of a cycle isn’t totally glad, it moves once more to search out what it would like. As a result, each individual is dominated by motivation psychology.
Most of our motives have circular nature, they’re aroused, they trigger behavior that ends up in a goal or need, and eventually, once the goal or need is reached, they shut off or restart once more. The behavior that’s associated with drive state is termed “Instrumental behavior” as a result of its instrumental in delivery regarding the goal or the satisfaction of would like.
Types of Motivation Psychology
There are two styles of motivation psychology, Intrinsic motivation, and extrinsic motivation. It is vital to know that we tend to don’t seem to be all the same therefore effectively motivating your staff needs that you just gain associate degree understanding of the various styles of motivation psychology. Such associate degree understanding can alter you to categorize your team members and apply the suitable form of motivation psychology.
You may notice every member completely different and every member’s psychological feature wants are going to be varied likewise. Some folks respond best to intrinsic which implies “from within” and can meet any obligation of a part of their passion. Quite the reverse, others can respond higher to adscititious motivation that, in their world, provides that tough tasks may be restricted provided there’s an award upon completion of that task. Become associate degree knowledgeable in determinative which kind can work best with that team members.
Tips
All folk’s expertise fluctuations in their motivation and self will. Generally, you may feel discharged and extremely driven to achieve your goals, whereas at different times you may feel listless or unsure of what you wish or the way to succeed in it.
Even if you are feeling low on motivation psychology, there are steps you’ll take which will keep you moving forward. Some stuff you will do include:
- Adjust your goals to target things that actually concern you
- Improve your confidence
- Remind yourself regarding what you achieved within the past and what wherever your strengths lie
- If their square measure stuff you feel insecure regarding, strive to function by creating enhancements in those areas in order that you’re feeling a lot of competent and capable.
Some stuff you ought to watch for which may hurt your motivation psychology. These include:
- Quick fixes or all-or-nothing thinking. it is easy to feel unmotivated if you cannot fix one thing like a shot or if you cannot have it all right away. inform yourself that reaching your goals takes time.
- Thinking that one size fits all. simply because an approach or technique worked for somebody else doesn’t mean that it’ll work for you. If one thing is not serving you to reach your goals or is creating you are feeling unmotivated, seek for things that may work higher for you.
Talk to your doctor if you’re feeling symptoms of apathy and low mood that last longer than a fortnight. generally, a persistent lack of motivation may be tied to a psychological state condition like depression.
The 6 Key Ideas Behind Theories of Motivation Psychology
Researchers have developed a variety of theories to elucidate motivation psychology. Every individual theory tends to be rather restricted in scope. However, by staring at the key ideas behind every theory, you’ll be able to gain a stronger understanding of motivation as a full.
Motivation psychology is that the force that initiates, guides and maintains goal-oriented behaviors. It’s what causes North American countries to require action, whether or not to grab a snack to cut back hunger or enroll in school to earn a degree. The forces that lie below motivation may be biological, social, emotional, or psychological features in nature. Let’s take a glance at all.
1. Instinct Theory of Motivation
According to instinct theories, folks are a unit intended to behave in sure ways that as a result they’re evolutionarily programmed to try to do this. Associate in Nursing example of this within the animal world is seasonal migration. These animals don’t learn to try to do this, it’s instead Associate in Nursing inborn pattern of behavior. Instincts motivate some species to migrate at certain times every year. The most drawback with this theory is that it didn’t very make a case for behavior, it simply represented it.

By the Nineteen Twenties, instinct theories were brushed off in favor of alternative psychological feature theories, however up-to-date biological process psychologists still study the influence of biological science and heredity on human behavior.
2. Incentive Theory of Motivation
The incentive theory suggests that individuals are a unit intended to try to do things due to external rewards. For instance, you would possibly be intended to travel to figure day by day for the financial reward of being paid. Activity learning ideas like association and reinforcement play a very important role during this theory of motivation.
This theory shares some similarities with the behaviorist conception of conditioning. In conditioning, behaviors are a unit learned by forming associations with outcomes. Reinforcement strengthens a behavior whereas penalization weakens it.
While incentive theory is comparable, it instead proposes that individuals deliberately pursue sure courses of action so as to achieve rewards. The bigger the perceived rewards, the lot of powerful folks are units intended to pursue those reinforcements.
3. Drive Theory of Motivation
It was once a dominant force in psychology. All human behavior is a product of biological need and anxiety created by the need. For instance, you would possibly be intended to drink a glass of water so as to cut back the interior state of thirst.
This theory is helpful in explaining behaviors that have a robust biological element, like hunger or thirst. The matter with the drive theory of motivation is that these behaviors aren’t continuously intended strictly by physiological wants. For instance, folks typically eat even once they aren’t very hungry.
4. Arousal Theory of Motivation
When arousal levels get too low, for instance, someone would possibly watch Associate in Nursing exciting flick or choose a jog. Once arousal levels get too high, on the opposite hand, someone would in all probability search for ways to relax like meditating or reading a book.

According to this theory, we have a tendency to area units intended to keep up Associate in the Nursing best level of arousal, though this level will vary if supported by the individual or true.
5. Humanistic Theory of Motivation
Humanistic theories of motivation area unit support the concept that individuals even have robust psychological feature reasons to perform numerous actions this can be magnificently illustrated in patriarch Maslow’s hierarchy of wants, which presents totally different|completely different} motivations at different levels.
First, folks are a unit intended to meet basic biological wants for food and shelter, yet as those of safety, love, and esteem. Once the lower-level needs are met, the first inducement becomes the requirement for self-actualization, or the will to meet one’s individual potential.
6. Expectancy Theory of Motivation
The expectancy theory of motivation suggests that once we are a unit puzzling over the longer term, we have a tendency to formulate completely different expectations regarding what we predict can happen. Once we predict that there’ll presumably be a positive outcome, we have a tendency to believe that we have a tendency to be a unit able to create that attainable future a reality. This leads folks to feel a lot of intent to pursue those probable outcomes.

The theory proposes that motivations include three key elements: valence, instrumentality, and expectancy. Valence refers to the worth folk’s place on the potential outcome. Things that appear unlikely to provide personal profit have an occasional valence, whereas those who supply immediate personal rewards have the next valence.
Instrumentality refers to if folks believe that they need a job to play within the foreseen outcome. If the event looks random or outside of the individual’s management, folks can feel less intended to pursue that course of action. If the individual plays a serious role within the success of the endeavor, however, folks can feel a lot of instrumental within the method.
Expectancy is that the belief that one has the capabilities to provide the end result. If folks desire they lack the abilities or information to realize the specified outcome, they’re going to be less intended to do so. Those that feel capable, on the opposite hand, are going to be a lot of things to do to succeed in that goal.
Conclusion
Understanding motivation psychology is very important in several areas of life, from parenting to the geographical point. You’ll need to line the simplest goals and establish the proper reward systems to inspire others further to increase your own motivation psychology.
Knowledge of motivating factors and manipulating them is employed in selling and different aspects of business psychological science. It’s square measure wherever there are several myths and everybody will enjoy knowing what works and what does not.
References:
https://www.managementnote.com
https://kylescoffeelosophies.wordpress.com




